Event Driven Programming"
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
'''''Event Handling Instructions''''' | '''''Event Handling Instructions''''' | ||
| − | *From the request, the ZK upload engine knows '''which component''' fired the event and '''what event''' is fired. It also knows how to handle this request because we've specified the event handling code in ZUL using EL (Expression Language): "lbl.value = self.label", which translates | + | *From the request, the ZK upload engine knows '''which component''' fired the event and '''what event''' is fired. It also knows how to handle this request because we've specified the event handling code in ZUL using EL (Expression Language): "lbl.value = self.label", which translates tino the following Java code: |
<source lang="java"> | <source lang="java"> | ||
lbl.setValue(self.getLabel); | lbl.setValue(self.getLabel); | ||
Revision as of 03:39, 19 July 2011
![]() This article is out of date, please refer to http://books.zkoss.org/zkessentials-book/master/ for more up to date information.
This article is out of date, please refer to http://books.zkoss.org/zkessentials-book/master/ for more up to date information.
In the previous section, we saw how components are declared in ZK User Interface Markup Language (ZUML) to compose an application's user interface. Now we'll look into ZK's event driven programming model to make all the components in an application work together to bring full base functionality to our cause.
How Event Driven Programming Works with Request/Response
Event driven programming is widely adopted for responsive GUI experience. Each ZK component is acceptable to have one or more event listeners registered to itself. A component registered with an event listener will listen to actions from users or events registered by the ZK framework itself. The event driven programming model in ZK works perfectly with the Request-Response model of HTTP.
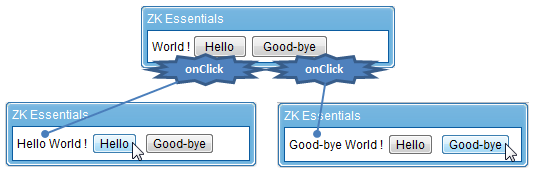
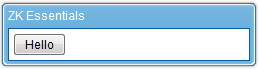
Take the sample we saw in the previous section:
<window title="ZK Essentials" mode="overlapped" border="normal" width="250px">
<label id="lbl"/>World !
<button label="Hello " onClick="lbl.value = self.label"/>
<button label="Good-bye " onClick="lbl.value = self.label"/>
</window>
The functionality for this sample code displays the strings of text the user has selected and the text is displayed in a label.

Breaking down how the event driven model works
Register Event Listeners
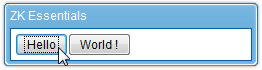
- At line 3 and 4, we register the onClick events on the buttons so we'll know when and which button is clicked.
<button label="Hello " onClick="lbl.value = self.label"/>
<button label="Good-bye " onClick="lbl.value = self.label"/>
Event Sent with Request
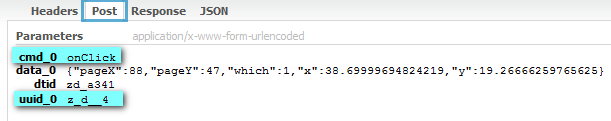
- When the user clicks one of the buttons, its respective onClick event is sent to the server for processing by default (optionally, we could handle events from the client directly). As shown highlighted in blue, the "onClick" event and the button's UUID (Universal Unique Identifier) is sent by the Ajax request.
- From the request, the ZK upload engine knows which component fired the event and what event is fired. It also knows how to handle this request because we've specified the event handling code in ZUL using EL (Expression Language): "lbl.value = self.label", which translates tino the following Java code:
lbl.setValue(self.getLabel);
- Where lbl is the ID we assigned to the Label component and self refers to the Button component itself (akin to this in Java)
Update Instruction Sent Back in Response
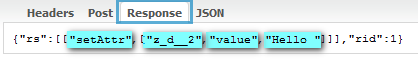
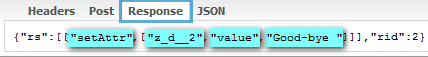
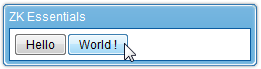
- The server then sends the instructions back to the client to reflect this change in the label's value:
- Where the instructions tell the client engine to set the attribute "value" to "Hello" for the component with the UUID "z_d__2", which is the label component.
How to Register Event Listeners
Various ways are provided in ZK to register and handle events, we'll look into the most common usages here.
Event Handling in ZUL page
In a ZUL file, an event handler is registered to a component as the component's attribute.
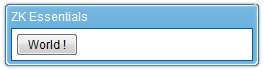
For example, suppose we have a button labeled "Hello", and we want to create a button labeled "World !" dynamically when the "Hello" button is clicked.
We could program this behavior entirely in a ZUL file:
<window id="win" title="ZK Essentials" border="normal" width="250px">
<button label="Hello">
<attribute name="onClick">
<![CDATA[
Button btn = new Button();
btn.setLabel("World !");
btn.setParent(win);
]]>
</attribute>
</button>
</window>
Inside the button declaration, we declare the "onClick" event as the button's attribute and code its event handling instructions directly in ZUL. This is possible because the Java code is interpreted by BeanShell dynamically. In the Java code, we first created a new Button, set its label to "World !", and then set the Window component as its parent. Although convenient, registering event right in ZUL is not recommended if your application is performance sensitive. As all the Java code needs to be interpreted dynamically.
Event Handling In a Controller
Following the ZK MVC pattern, we create a controller class where the event is forwarded to it for handling.
So here we make the necessary changes:
- At line 1, we declared: apply=controller class name so that the events fired within the window is all forwarded to the controller for event handling.
- At line 2, we need to give the "Hello" button an ID so the controller would know which button fired the onClick event.
<window id="win" title="ZK Essentials" border="normal" width="250px" apply="demo.zkoss.SampleCtrl">
<button id="helloBtn" label="Hello"/>
</window>
We then implement our controller class:
- At line 7, we extend the GenericForwardComposer so all events fired in its applied component would be forwarded here.
- At line 9, we declare the Window variable to match that we declared for the Window component's ID so they are wired.
- At line 11, we follow ZK's convention for naming the event handler 'event_name$component_id'
- From line 12 to 14, we use the same Java code we did previously to dynamically create a button.
package demo.zkoss;
import org.zkoss.zk.ui.util.GenericForwardComposer;
import org.zkoss.zul.Button;
import org.zkoss.zul.Window;
public class SampleCtrl extends GenericForwardComposer {
Window win;
public void onClick$helloBtn(){
Button btn = new Button();
btn.setLabel("World !");
btn.setParent(win);
}
}
Event Handling of Dynamically Generated Components
Suppose we take our previous example a step further, we would like to clear off the "Hello" button in the window when we click the dynamically created "World !" button. We'll need to register an event listener to the dynamically created "World !" button.
- At line 10, we add a new event listener to the newly created button. The addEventListener method takes an event name (String) and an EventListener as its arguments.
- Within the anonymous EventListener class, we implement the onEvent method to have the Window component fetch its "fellow" component "helloBtn" and call its detach method to clear off the Window component.
public class SampleCtrl extends GenericForwardComposer {
Window win;
public void onClick$helloBtn(){
Button btn = new Button();
btn.setLabel("World !");
btn.setParent(win);
btn.addEventListener("onClick", new EventListener(){
public void onEvent(Event event) throws Exception {
win.getFellow("helloBtn").detach();
}
});
}
}