Customizing Bootstrap Theme Demonstration"
Raymondchao (talk | contribs) |
m (correct highlight (via JWB)) |
||
| (61 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Template: | + | {{Template:Smalltalk_Author| |
| + | |author=Raymond Chao, Engineer, Potix Corporation | ||
| + | |date=November 26, 2013 | ||
| + | |version=ZK 7.0.0 (or latest) | ||
| + | }} | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| − | ZK 7 is an upcoming | + | ZK 7 is an upcoming major release focusing on HTML5 and CSS3. Previously we have demonstrated how to use ZK 7′s new theme system with Bootstrap & CSS3 in this [http://blog.zkoss.org/index.php/2013/08/13/zk-7-new-theme-system-with-bootstrap-css-3/ blog] and we also provided a [http://blog.zkoss.org/index.php/2013/09/03/zk-7-zk-components-x-bootstrap-3/ guide] with more details on how to integrate ZK components and Bootstrap 3. In this small talk, we will customize another theme to look like one coming from [https://wrapbootstrap.com/ {'''wrap'''}bootstrap]. |
| + | |||
| + | == Demo == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gflash width="700" height="500" >CBTDSmalldemo.swf</gflash> | ||
| + | |||
| + | High-quality video can be found [/_w/images/3/30/CBTDdemo.swf here] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Live demo can be found [http://www.zkoss.org/ui-examples/applications2/ here] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other ZK 7 related demos can be found [http://www.zkoss.org/zkdemo/customize_theme here] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Note''': This demo design is referenced from [https://wrapbootstrap.com/theme/ace-responsive-admin-template-WB0B30DGR Ace - Responsive Admin Template - WB0B30DGR] | ||
== Prerequisites == | == Prerequisites == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 25: | ||
* Bootstrap 3 knowledge, read [http://getbootstrap.com/getting-started/ here] | * Bootstrap 3 knowledge, read [http://getbootstrap.com/getting-started/ here] | ||
* LESS language, read [http://lesscss.org/ here] | * LESS language, read [http://lesscss.org/ here] | ||
| + | * ZK Style Customization knowledge, read [http://books.zkoss.org/wiki/ZK_Style_Customization_Guide here] | ||
== Design Template == | == Design Template == | ||
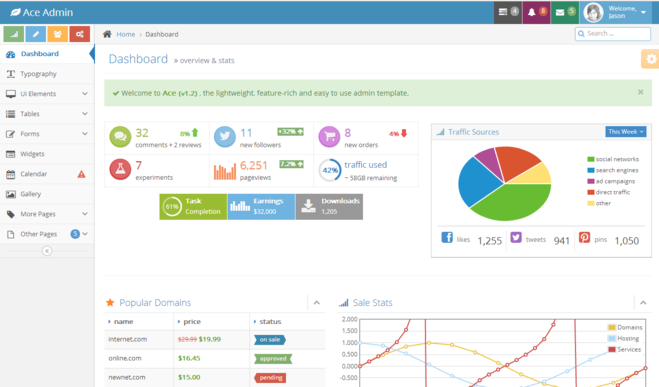
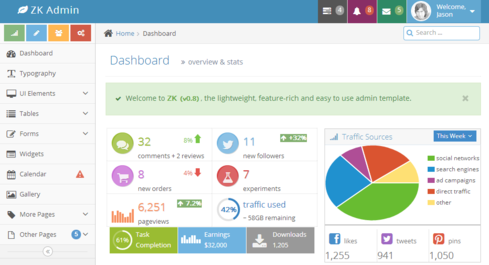
| − | We picked [https://wrapbootstrap.com/theme/ace-responsive-admin-template-WB0B30DGR Ace Template] from {'''wrap'''}bootstrap as our design template. In this demonstration, we will customize the Dashboard page with Pure ZK and CSS3. | + | We picked [https://wrapbootstrap.com/theme/ace-responsive-admin-template-WB0B30DGR Ace Template] from {'''wrap'''}bootstrap as our design template. The theme's styling is a bit complicated, so we can take a deeper look at ZK's new theme system by customizing a theme according to the template. In this demonstration, we will customize the Dashboard page with Pure ZK and CSS3. |
[[File:AcePreview.png|659x387px]] | [[File:AcePreview.png|659x387px]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Analyze Layout == | == Analyze Layout == | ||
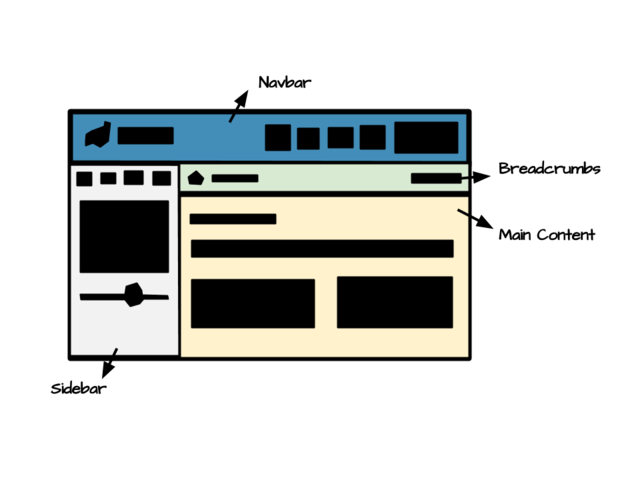
| − | + | This layout can be separated into 4 sections. | |
[[File:CBTDLayout.png|640x480px]] | [[File:CBTDLayout.png|640x480px]] | ||
* Navbar | * Navbar | ||
| − | ** A | + | ** A logo on the left side |
| − | ** A set of menu navigation | + | ** A set of menu navigation on the right |
* Sidebar | * Sidebar | ||
| − | ** | + | ** Four button shourtcuts |
** Navigation bar | ** Navigation bar | ||
** Collapsed button | ** Collapsed button | ||
| Line 34: | Line 49: | ||
* Content | * Content | ||
** Header | ** Header | ||
| − | ** | + | ** Alert |
** Infobox | ** Infobox | ||
** Panel | ** Panel | ||
| − | ** | + | ** Tabs |
| − | According to the analysis, we combined ZK components < | + | According to the analysis, we combined ZK components <code>hlayout</code> and <code>vlayout</code> to layout the the structure of the page, then assigned <code>hflx="1"</code> to recalculate its width when resizing. Component <code>include</code> is also used to include each part's content. |
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
<include src="navbar.zul"/> | <include src="navbar.zul"/> | ||
<hlayout id="main" spacing="0"> | <hlayout id="main" spacing="0"> | ||
| − | + | <include src="sidebar.zul"/> | |
| − | + | <vlayout spacing="0" hflex="1"> | |
| − | + | <include src="breadcrumbs.zul"/> | |
| − | + | <include src="content.zul"/> | |
| − | + | </vlayout> | |
</hlayout> | </hlayout> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
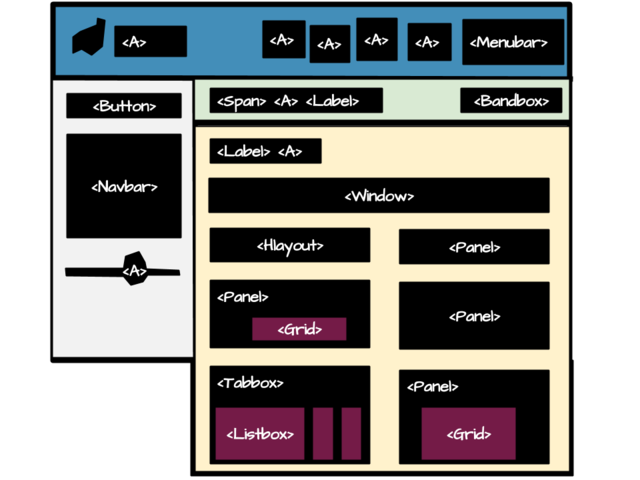
| − | == Implement with ZK | + | == Implement with ZK Components == |
| − | After | + | After constructing the basic layout, we can now implement content into each part with various ZK components. |
[[File:CBTDImpl.png|640x480px]] | [[File:CBTDImpl.png|640x480px]] | ||
| Line 60: | Line 75: | ||
[[File:CBTDBefore.png|489x296px]] | [[File:CBTDBefore.png|489x296px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Tips for Customization == | ||
| + | Before the start of customization, we provide some tips which may be helpful for users who want to create their own themes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Refer ZK Component's Less File === | ||
| + | The ZK theme maven project consists of all the ZK Component's less files. Referring the less files, you can understand and revise component's styling easily. Please refer this [http://blog.zkoss.org/index.php/2013/09/17/zk7-create-a-new-a-theme-project/ blog] to create a new theme project. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Use Sclass and Zclass Pattern === | ||
| + | Using CSS class rule with <code>sclass zclass</code> pattern can get higher priority level to apply to the component's class. For example: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="css" highlight="1"> | ||
| + | .comments.z-grid { | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Put an icon in the span === | ||
| + | If we want to display the icon only, it can be placed in the span with <code>.z-icon-xxx</code> sclass or zclass. For example: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="xml" line="false"> | ||
| + | <span zclass="z-icon-comments"/> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Adjust Popup's position === | ||
| + | There are two ways to dictate the position for ZK's popup. One is by specifying the relative position and the reference component( <code>position=after_end</code>), another is by giving a specific position( <code>x=100, y=40</code>) directly. We can use the position attribute and style popup's margin to adjust popup's position. | ||
| + | For example, we can use relative position to make the popup to appear below the button, aligned to the right. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:CBTDPopupPosBefore.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="xml" highlight="1"> | ||
| + | <button sclass="btn-primary" iconSclass="z-icon-cog" popup="cogtt, position=after_end, type=toggle"/> | ||
| + | <popup id="cogtt" sclass="cog"> | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | </popup> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Style the popup's margin to adjust popup's position. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="css" highlight="2"> | ||
| + | .cog.z-popup { | ||
| + | margin-left: 4px; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:CBTDPopupPosAfter.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Use Pseudo-Element === | ||
| + | Using <code>:before</code> and <code>:after</code> can add an element before or after a component, they decorate the component without the need of changing its DOM structure. For example. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:CBTDNavPseudo.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="xml" highlight="3"> | ||
| + | <navbar> | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | <nav label="Other Pages" badgeText="5" iconSclass="z-icon-file-o"> | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | </navbar> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="css" highlight="2"> | ||
| + | // Add an angel down icon after the Nav | ||
| + | .z-nav-text:after { | ||
| + | .baseIconFont(); | ||
| + | .iconFontStyle(18px, #666); | ||
| + | .displaySize(inline-block, 14px, 14px); | ||
| + | content: "\f107"; | ||
| + | position: absolute; | ||
| + | line-height: 14px; | ||
| + | right: 11px; | ||
| + | top: 11px; | ||
| + | padding: 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>.baseIconFont()</code>, <code>.iconFontStyle()</code> and <code>.displaySize()</code> are useful rulesets defined in zk mixins. We can follow the [[#Import_LESS_Files | instruction]] to import them. | ||
== Customize Look And Feel == | == Customize Look And Feel == | ||
| − | In this section, we will mention the necessary preparations and some customized components as examples | + | In this section, we will mention the necessary preparations and some customized components as examples. |
[[File:CBTDAfter.png|489x296px]] | [[File:CBTDAfter.png|489x296px]] | ||
| − | === | + | === Import Fonts === |
| − | Before | + | Before customizing the look and feel, we need to import the Open Sans font from google server or download it to your folder directly. |
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="xml" line="false"> | ||
| + | <?link href="css/fonts.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"?> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Import LESS Files === | ||
| + | LESS is a dynamic stylesheet language, which extends CSS with dynamic behaviors such as variables, mixins, operations and functions. | ||
| + | Bootstrap and ZK have already defined many helpful variables and mixins for usage. We can import them to reuse the code instead of reinventing the wheel. ZK's variables and mixins can be obtained from ZK's theme maven project, please refer [http://blog.zkoss.org/index.php/2013/09/17/zk7-create-a-new-a-theme-project/ here]. | ||
| + | |||
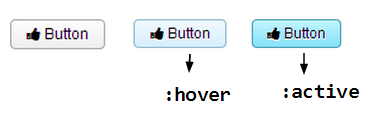
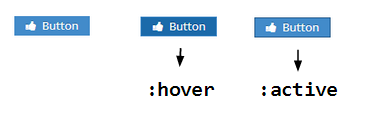
| + | === Customize Button === | ||
| + | ZK button's default style contains gradient background and rounded corners. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:CBTDButtonBefore.png]] | ||
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
| − | < | + | <button iconSclass="z-icon-thumbs-up" label="Button"/> |
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | + | We need to remove the gradient background and rounded corners, then mimic the css from bootstrap and ace template. <code>.borderRadius(0)</code>, <code>.transition(all, ease, .15s)</code> and <code>.resetGradient()</code> are built-in rulesets defined in zk mixins. | |
| − | We mimic the | + | |
<source lang="css"> | <source lang="css"> | ||
.z-button { | .z-button { | ||
| − | + | position: relative; | |
| − | + | padding: 3px 12px; | |
| − | + | .borderRadius(0); | |
| − | + | text-shadow: 0 -1px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.25); | |
| − | + | min-height: 0; | |
| − | + | color: #FFF !important; | |
| − | + | .transition(all, ease, .15s); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | &:active { | |
| − | + | top: 1px; | |
| − | + | left: 1px; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | &, &:hover, &:focus, &:active { | |
| − | + | .resetGradient(); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | /* Icon in the button */ | |
| − | + | > [class*="z-icon-"] { | |
| − | + | display: inline; | |
| − | + | margin-right: 4px; | |
| − | + | } | |
} | } | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | === Progressmeter === | + | After applying the style, the button's background would become transparent. |
| − | To | + | |
| + | [[File:CBTDButtonTransparent.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then, assign <code>btn-primiry</code> or other CSS class to the button's sclass attribute which will create a colored button. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:CBTDButtonAfter.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="xml"> | ||
| + | <button iconSclass="z-icon-thumbs-up" label="Button" sclass="btn-primary"/> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="css"> | ||
| + | .btn-color(@color-name) { | ||
| + | @color1-name : ~`"btn-@{color-name}"`; | ||
| + | @color2-name : ~`"btn-@{color-name}-hover"`; | ||
| + | |||
| + | .btn-color(@@color1-name, @@color2-name); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .btn-primary { | ||
| + | .btn-color(~"primary"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
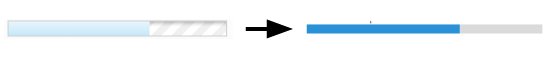
| + | === Customize Progressmeter === | ||
| + | To customize <code>progressmeter</code>, we change its height, background color and remove its border line. | ||
[[File:CBTDProgressMeter.png]] | [[File:CBTDProgressMeter.png]] | ||
| − | <source lang="xml"> | + | <source lang="xml" line="false"> |
<progressmeter value="65" width="100%"/> | <progressmeter value="65" width="100%"/> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | <source lang="css"> | + | <source lang="css" line="false"> |
.z-progressmeter { | .z-progressmeter { | ||
height: 9px; | height: 9px; | ||
| Line 120: | Line 249: | ||
&-image { | &-image { | ||
display: inline-block; | display: inline-block; | ||
| + | .resetGradient(); | ||
background-color: #2A91D8; | background-color: #2A91D8; | ||
| − | |||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | + | === Customize Tooltip === | |
| − | === Tooltip === | + | The original look and feel of ZK's tooltip is totally different from the one that's in the demo. The easiest way to customize a tooltip's look is by assigning a [http://books.zkoss.org/wiki/ZK_Style_Guide/ZK_Class_Concept zclass] <code>tooltip</code> to it. |
| − | The ZK | ||
[[File:CBTDTooltip.png]] | [[File:CBTDTooltip.png]] | ||
| − | <source lang="xml"> | + | <source lang="xml" line="false"> |
<popup zclass="tooltip" sclass="left tooltip-success"> | <popup zclass="tooltip" sclass="left tooltip-success"> | ||
| − | + | <span zclass="tooltip-arrow"/> | |
| − | + | <label zclass="tooltip-inner" value="Mark as done"/> | |
</popup> | </popup> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | + | <source lang="css" line="false"> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <source lang="css"> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
.tooltip-success.tooltip { | .tooltip-success.tooltip { | ||
> .tooltip-content >.tooltip-inner { | > .tooltip-content >.tooltip-inner { | ||
| − | background-color: @tooltip-success-color; | + | background-color:@tooltip-success-color; |
color:#FFF; | color:#FFF; | ||
text-shadow:1px 1px 0 rgba(60,100,20,0.3); | text-shadow:1px 1px 0 rgba(60,100,20,0.3); | ||
| Line 162: | Line 281: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | + | The <code>span</code> component inside the popup's job is to display a triangle as an arrow of the tooltip. | |
| − | |||
| − | [[File:CBTDTabboxBefore.png]] | + | [[File:CBTDTooltipCss.png]] |
| + | |||
| + | Bootstrap tooltip's opacity level is zero. We should change the opacity to 1 to make it visible when the tooltip shows up. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="css" highlight="2"> | ||
| + | .tooltip { | ||
| + | .opacity(1) !important; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Customize Tabbox === | ||
| + | When Tabbox is in its default orientation, the row of tabs displays on the top left-hand side, illustrated below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:CBTDTabboxBefore.png|center|frame]] | ||
| − | <source lang="xml"> | + | <source lang="xml" line="false"> |
| − | <a label="RECENT" iconSclass="z-icon-rss orange | + | <a label="RECENT" iconSclass="z-icon-rss orange" sclass="rcaption lighter"/> |
| − | |||
<tabbox sclass="rtab"> | <tabbox sclass="rtab"> | ||
| − | + | <tabs> | |
| − | + | <tab label="Tasks"/> | |
| − | + | <tab label="Members"/> | |
| − | + | <tab label="Comments"/> | |
| − | + | </tabs> | |
| − | + | <tabpanels> | |
| − | + | <tabpanel><!-- Tasks content --></tabpanel> | |
| − | + | <tabpanel><!-- Menbers content --></tabpanel> | |
| − | + | <tabpanel><!-- Comments content --></tabpanel> | |
| − | + | </tabpanels> | |
</tabbox> | </tabbox> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | If we want to move | + | If we want to move these tabs to the top right-hand side, we can float each tab to the right. |
| − | [[File:CBTDTabboxFloat.png]] | + | [[File:CBTDTabboxFloat.png|center|frame]] |
| − | <source lang="css" | + | <source lang="css" highlight=3> |
.rtab.z-tabbox { | .rtab.z-tabbox { | ||
.z-tab { | .z-tab { | ||
| Line 196: | Line 326: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | After | + | After floating each tab to the right, the first tab would be pulled to the rightmost side. Hence, the order of tabs should be inversed, and the last tab should be selected as default. |
| − | [[File:CBTDTabboxInverse.png]] | + | [[File:CBTDTabboxInverse.png|center|frame]] |
| − | <source lang="xml"> | + | <source lang="xml" highlight="4,5,6,9,10,11"> |
| − | <a label="RECENT" iconSclass="z-icon-rss orange | + | <a label="RECENT" iconSclass="z-icon-rss orange" sclass="rcaption lighter"/> |
| − | |||
<tabbox sclass="rtab"> | <tabbox sclass="rtab"> | ||
| − | + | <tabs> | |
| − | + | <tab label="Comments"/> | |
| − | + | <tab label="Members"/> | |
| − | + | <tab label="Tasks" selected="true"/> | |
| − | + | </tabs> | |
| − | + | <tabpanels> | |
| − | + | <tabpanel><!-- Comments content --></tabpanel> | |
| − | + | <tabpanel><!-- Menbers content --></tabpanel> | |
| − | + | <tabpanel><!-- Tasks content --></tabpanel> | |
| − | + | </tabpanels> | |
</tabbox> | </tabbox> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | The header and tabbox | + | The header and tabbox needs to be displayed horizontally side by side, so tabbox's position should be absolute and set top to zero. |
| − | <source lang="css"> | + | [[File:CBTDTabboxAbs.png|center|frame]] |
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="css" highlight="2,3"> | ||
.rtab.z-tabbox { | .rtab.z-tabbox { | ||
position: absolute; | position: absolute; | ||
| Line 226: | Line 357: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | |||
Finally, customize the look and feel. | Finally, customize the look and feel. | ||
| − | [[File:CBTDTabboxAfter.png]] | + | [[File:CBTDTabboxAfter.png|center|frame]] |
| + | |||
| + | === Customize Scrollbar === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ZK7 introduces the '''fake''' scrollbar in <code>meshwidget</code> and <code>borderlayout</code>, it behaves as the browser's native scrollbar. '''Fake''' scrollbars are also customizable in style, in this demo we have styled the scrollbar into a much thinner and simpler and 'flat' scrollbar. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:CBTDScrollbar.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Styling the scrollbar consists of the following five steps: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Hide all the icons | ||
| + | # Move the wrapper to the top | ||
| + | # Make the backgroud transparent | ||
| + | # Simplify indicator | ||
| + | # Slim down the scrollbar | ||
| − | == Functionality Code == | + | [[File:CBTDScrollbarCss.png|338x274px]] |
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="css" line="false"> | ||
| + | .z-scrollbar.z-scrollbar-vertical { | ||
| + | width: 7px; | ||
| + | .z-scrollbar-up, .z-scrollbar-down, | ||
| + | .z-scrollbar-icon, .z-scrollbar-rail { | ||
| + | display: none; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | .z-scrollbar-wrapper { | ||
| + | top: 0; | ||
| + | .z-scrollbar-indicator { | ||
| + | width: 7px; | ||
| + | background-image: none; | ||
| + | background-color: #999; | ||
| + | border: 0; | ||
| + | border-radius: 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | .z-scrollbar-rail { | ||
| + | background-color: transparent; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Functionality Code Fragments == | ||
| + | Although in most cases we don't have to write any code, we still need to declare some functions to manipulate components in some situations. | ||
=== Add open class to navbar menu === | === Add open class to navbar menu === | ||
| − | We | + | We declared an event handler in popup which will be notified when onOpen event occurs, it will toggle the open sclass to the anchor component. |
| − | So the | + | So the component's background will be darken when its popup is showing up. |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:CBTDOpenClass.png]] | ||
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
| − | <a id="atask" iconSclass="z-icon-tasks" popup="taskpp, position=after_end" sclass="grey"> | + | <a id="atask" iconSclass="z-icon-tasks" popup="taskpp, position=after_end, type=toggle" sclass="grey"> |
| − | + | <label value="4" sclass="badge badge-grey"/> | |
</a> | </a> | ||
| − | <popup id=" | + | <popup id="notipp" sclass="menu menu-pink" width="240px"> |
| − | + | ... | |
</popup> | </popup> | ||
| − | < | + | </source> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | // Toggle open | + | <source lang="java"> |
| − | void | + | @Listen("onOpen = #taskpp") |
| − | + | public void toggleTaskPopup(OpenEvent event) { | |
| − | + | toggleOpenClass(event.isOpen(), atask); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | // Toggle open class to the component | |
| − | + | public void toggleOpenClass(Boolean open, Component component) { | |
| + | HtmlBasedComponent comp = (HtmlBasedComponent) component; | ||
| + | String scls = comp.getSclass(); | ||
| + | if (open) { | ||
| + | comp.setSclass(scls + " open"); | ||
| + | } else { | ||
| + | comp.setSclass(scls.replace(" open", "")); | ||
| + | } | ||
} | } | ||
| − | |||
</source> | </source> | ||
=== Implement Collapse Mechanism === | === Implement Collapse Mechanism === | ||
| − | The sidebar is collapsible, user can click the button in the bottom of navbar to collapse or expand sidebar | + | The sidebar in this demo is collapsible, user can click the button in the bottom of the navbar to collapse or expand the sidebar, illustrated in the picture below: |
[[File:Collapsible.png|640x480px]] | [[File:Collapsible.png|640x480px]] | ||
| − | + | We need to declare <code>toggleSidebarCollapsed()</code> to proceed the action, like the following: | |
<source lang="java"> | <source lang="java"> | ||
| − | void toggleSidebarCollapsed() { | + | // Toggle sidebar to collapse or expand |
| − | + | @Listen("onClick = #toggler") | |
| − | + | public void toggleSidebarCollapsed() { | |
| − | + | if (navbar.isCollapsed()) { | |
| − | + | sidebar.setSclass("sidebar"); | |
| − | + | navbar.setCollapsed(false); | |
| − | + | calitem.setTooltip("calpp, position=end_center, delay=0"); | |
| − | + | toggler.setIconSclass("z-icon-angle-double-left"); | |
| − | + | } else { | |
| − | + | sidebar.setSclass("sidebar sidebar-min"); | |
| − | + | navbar.setCollapsed(true); | |
| − | + | calitem.setTooltip(""); | |
| − | + | toggler.setIconSclass("z-icon-angle-double-right"); | |
| + | } | ||
| + | // Force the hlayout contains sidebar to recalculate its size | ||
| + | Clients.resize(sidebar.getRoot().query("#main")); | ||
} | } | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | Because < | + | Because <code>Navbar</code> is collapsible, <code>isCollapsed()</code> can determine whether <code>navbar</code> is collapsed or not. If not, we can easily call <code>setCollapsed(true)</code> to collapse it. When <code>navbar</code> is collapsed, its children will only appear as icon and badges. The text part will appear when you mouse hover the icon. Next, we need remove the tooltip of <code>Navitem</code> to prevent it from showing up with text when hovering. Then, add <code>sidebar-min</code> class to <code>sidebar</code> and change the toggler's icon. In the end, <code>Clients.resize(sidebar.getRoot().query("#main"))</code> will force the client to recalculate the size of the main content. |
| − | The shortcuts also | + | The shortcuts are also collapsed, so an additional set of collapsed shortcuts is needed for display when the sidebar is collapsed. If user mouses over the collapsed shortcuts, the shortcuts will expand. |
[[File:CBTDShortcutsFun.png]] | [[File:CBTDShortcutsFun.png]] | ||
| Line 293: | Line 473: | ||
<source lang="xml"> | <source lang="xml"> | ||
<div class="shortcuts"> | <div class="shortcuts"> | ||
| − | + | <div class="shortcuts-expanded"> | |
| − | + | <button type="button" class="btn-success" iconSclass="z-icon-signal"/> | |
| − | + | <button type="button" class="btn-info" iconSclass="z-icon-pencil"/> | |
| − | + | <button type="button" class="btn-warning" iconSclass="z-icon-group"/> | |
| − | + | <button type="button" class="btn-danger" iconSclass="z-icon-cogs"/> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | <div class="shortcuts-collapsed"> | |
| − | + | <button type="button" class="btn-success"/> | |
| − | + | <button type="button" class="btn-info"/> | |
| − | + | <button type="button" class="btn-warning"/> | |
| − | + | <button type="button" class="btn-danger"/> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
</div> | </div> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Conclusion == | ||
| + | In this demo, we used ZK 7 with bootstrap and CSS3 to customize a bootstrap theme from scratch. We analyzed the template and implemented it with ZK components, then styled the look and feel using CSS3. This small talk shows you the power and flexibility of ZK 7's new theme system, and how you can customize your own personal or corporate theme with CSS3, LESS and bootstrap easily. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Example Source == | ||
| + | Source code can be found in [https://github.com/jumperchen/ui-examples Github] and the layout design is owned by [https://wrapbootstrap.com/theme/ace-responsive-admin-template-WB0B30DGR EasyMind]. Please contact the designer directly if you wish to use his design template commercially. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Reference == | ||
| + | * [https://wrapbootstrap.com/theme/ace-responsive-admin-template-WB0B30DGR Ace - Responsive Admin Template - WB0B30DGR] | ||
| + | * [http://getbootstrap.com/getting-started/ Bootstrap] | ||
| + | * [http://lesscss.org/ LESS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Comments= | ||
| + | {{#tag:comment | ||
| + | |http://books.zkoss.org/wiki/{{SUBJECTPAGENAME}}|disqus=1 | ||
| + | |}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:ZK]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Theme]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Template:Smalltalk_Footer| | ||
| + | |name=Potix Corporation | ||
| + | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 04:20, 20 January 2022
Raymond Chao, Engineer, Potix Corporation
November 26, 2013
ZK 7.0.0 (or latest)
Introduction
ZK 7 is an upcoming major release focusing on HTML5 and CSS3. Previously we have demonstrated how to use ZK 7′s new theme system with Bootstrap & CSS3 in this blog and we also provided a guide with more details on how to integrate ZK components and Bootstrap 3. In this small talk, we will customize another theme to look like one coming from {wrap}bootstrap.
Demo
High-quality video can be found [/_w/images/3/30/CBTDdemo.swf here]
Live demo can be found here
Other ZK 7 related demos can be found here
Note: This demo design is referenced from Ace - Responsive Admin Template - WB0B30DGR
Prerequisites
- ZK 7.0.0-RC version or later
- Bootstrap 3 knowledge, read here
- LESS language, read here
- ZK Style Customization knowledge, read here
Design Template
We picked Ace Template from {wrap}bootstrap as our design template. The theme's styling is a bit complicated, so we can take a deeper look at ZK's new theme system by customizing a theme according to the template. In this demonstration, we will customize the Dashboard page with Pure ZK and CSS3.
Analyze Layout
This layout can be separated into 4 sections.
- Navbar
- A logo on the left side
- A set of menu navigation on the right
- Sidebar
- Four button shourtcuts
- Navigation bar
- Collapsed button
- Breadcrumbs
- Breadcrumb
- Search input
- Content
- Header
- Alert
- Infobox
- Panel
- Tabs
According to the analysis, we combined ZK components hlayout and vlayout to layout the the structure of the page, then assigned hflx="1" to recalculate its width when resizing. Component include is also used to include each part's content.
<include src="navbar.zul"/>
<hlayout id="main" spacing="0">
<include src="sidebar.zul"/>
<vlayout spacing="0" hflex="1">
<include src="breadcrumbs.zul"/>
<include src="content.zul"/>
</vlayout>
</hlayout>
Implement with ZK Components
After constructing the basic layout, we can now implement content into each part with various ZK components.
And it will look like this:
Tips for Customization
Before the start of customization, we provide some tips which may be helpful for users who want to create their own themes.
Refer ZK Component's Less File
The ZK theme maven project consists of all the ZK Component's less files. Referring the less files, you can understand and revise component's styling easily. Please refer this blog to create a new theme project.
Use Sclass and Zclass Pattern
Using CSS class rule with sclass zclass pattern can get higher priority level to apply to the component's class. For example:
.comments.z-grid {
...
}
Put an icon in the span
If we want to display the icon only, it can be placed in the span with .z-icon-xxx sclass or zclass. For example:
1 <span zclass="z-icon-comments"/>
Adjust Popup's position
There are two ways to dictate the position for ZK's popup. One is by specifying the relative position and the reference component( position=after_end), another is by giving a specific position( x=100, y=40) directly. We can use the position attribute and style popup's margin to adjust popup's position.
For example, we can use relative position to make the popup to appear below the button, aligned to the right.
<button sclass="btn-primary" iconSclass="z-icon-cog" popup="cogtt, position=after_end, type=toggle"/>
<popup id="cogtt" sclass="cog">
...
</popup>
Style the popup's margin to adjust popup's position.
.cog.z-popup {
margin-left: 4px;
}
Use Pseudo-Element
Using :before and :after can add an element before or after a component, they decorate the component without the need of changing its DOM structure. For example.
<navbar>
...
<nav label="Other Pages" badgeText="5" iconSclass="z-icon-file-o">
...
</navbar>
// Add an angel down icon after the Nav
.z-nav-text:after {
.baseIconFont();
.iconFontStyle(18px, #666);
.displaySize(inline-block, 14px, 14px);
content: "\f107";
position: absolute;
line-height: 14px;
right: 11px;
top: 11px;
padding: 0;
}
.baseIconFont(), .iconFontStyle() and .displaySize() are useful rulesets defined in zk mixins. We can follow the instruction to import them.
Customize Look And Feel
In this section, we will mention the necessary preparations and some customized components as examples.
Import Fonts
Before customizing the look and feel, we need to import the Open Sans font from google server or download it to your folder directly.
1 <?link href="css/fonts.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"?>
Import LESS Files
LESS is a dynamic stylesheet language, which extends CSS with dynamic behaviors such as variables, mixins, operations and functions. Bootstrap and ZK have already defined many helpful variables and mixins for usage. We can import them to reuse the code instead of reinventing the wheel. ZK's variables and mixins can be obtained from ZK's theme maven project, please refer here.
Customize Button
ZK button's default style contains gradient background and rounded corners.
<button iconSclass="z-icon-thumbs-up" label="Button"/>
We need to remove the gradient background and rounded corners, then mimic the css from bootstrap and ace template. .borderRadius(0), .transition(all, ease, .15s) and .resetGradient() are built-in rulesets defined in zk mixins.
.z-button {
position: relative;
padding: 3px 12px;
.borderRadius(0);
text-shadow: 0 -1px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.25);
min-height: 0;
color: #FFF !important;
.transition(all, ease, .15s);
&:active {
top: 1px;
left: 1px;
}
&, &:hover, &:focus, &:active {
.resetGradient();
}
/* Icon in the button */
> [class*="z-icon-"] {
display: inline;
margin-right: 4px;
}
}
After applying the style, the button's background would become transparent.
Then, assign btn-primiry or other CSS class to the button's sclass attribute which will create a colored button.
<button iconSclass="z-icon-thumbs-up" label="Button" sclass="btn-primary"/>
.btn-color(@color-name) {
@color1-name : ~`"btn-@{color-name}"`;
@color2-name : ~`"btn-@{color-name}-hover"`;
.btn-color(@@color1-name, @@color2-name);
}
.btn-primary {
.btn-color(~"primary");
}
Customize Progressmeter
To customize progressmeter, we change its height, background color and remove its border line.
1 <progressmeter value="65" width="100%"/>
1 .z-progressmeter {
2 height: 9px;
3 border: 0;
4 background-image: none;
5 background-color: #DADADA;
6
7 &-image {
8 display: inline-block;
9 .resetGradient();
10 background-color: #2A91D8;
11 }
12 }
Customize Tooltip
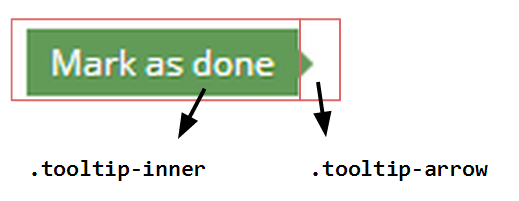
The original look and feel of ZK's tooltip is totally different from the one that's in the demo. The easiest way to customize a tooltip's look is by assigning a zclass tooltip to it.
1 <popup zclass="tooltip" sclass="left tooltip-success">
2 <span zclass="tooltip-arrow"/>
3 <label zclass="tooltip-inner" value="Mark as done"/>
4 </popup>
1 .tooltip-success.tooltip {
2 > .tooltip-content >.tooltip-inner {
3 background-color:@tooltip-success-color;
4 color:#FFF;
5 text-shadow:1px 1px 0 rgba(60,100,20,0.3);
6 border-radius: 0;
7 }
8 &.left .tooltip-arrow {
9 border-left-color: @tooltip-success-color;
10 }
11 }
The span component inside the popup's job is to display a triangle as an arrow of the tooltip.
Bootstrap tooltip's opacity level is zero. We should change the opacity to 1 to make it visible when the tooltip shows up.
.tooltip {
.opacity(1) !important;
}
Customize Tabbox
When Tabbox is in its default orientation, the row of tabs displays on the top left-hand side, illustrated below:
1 <a label="RECENT" iconSclass="z-icon-rss orange" sclass="rcaption lighter"/>
2 <tabbox sclass="rtab">
3 <tabs>
4 <tab label="Tasks"/>
5 <tab label="Members"/>
6 <tab label="Comments"/>
7 </tabs>
8 <tabpanels>
9 <tabpanel><!-- Tasks content --></tabpanel>
10 <tabpanel><!-- Menbers content --></tabpanel>
11 <tabpanel><!-- Comments content --></tabpanel>
12 </tabpanels>
13 </tabbox>
If we want to move these tabs to the top right-hand side, we can float each tab to the right.
.rtab.z-tabbox {
.z-tab {
float: right;
}
}
After floating each tab to the right, the first tab would be pulled to the rightmost side. Hence, the order of tabs should be inversed, and the last tab should be selected as default.
<a label="RECENT" iconSclass="z-icon-rss orange" sclass="rcaption lighter"/>
<tabbox sclass="rtab">
<tabs>
<tab label="Comments"/>
<tab label="Members"/>
<tab label="Tasks" selected="true"/>
</tabs>
<tabpanels>
<tabpanel><!-- Comments content --></tabpanel>
<tabpanel><!-- Menbers content --></tabpanel>
<tabpanel><!-- Tasks content --></tabpanel>
</tabpanels>
</tabbox>
The header and tabbox needs to be displayed horizontally side by side, so tabbox's position should be absolute and set top to zero.
.rtab.z-tabbox {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
...
Finally, customize the look and feel.
Customize Scrollbar
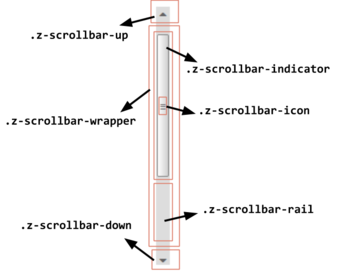
ZK7 introduces the fake scrollbar in meshwidget and borderlayout, it behaves as the browser's native scrollbar. Fake scrollbars are also customizable in style, in this demo we have styled the scrollbar into a much thinner and simpler and 'flat' scrollbar.
Styling the scrollbar consists of the following five steps:
- Hide all the icons
- Move the wrapper to the top
- Make the backgroud transparent
- Simplify indicator
- Slim down the scrollbar
1 .z-scrollbar.z-scrollbar-vertical {
2 width: 7px;
3 .z-scrollbar-up, .z-scrollbar-down,
4 .z-scrollbar-icon, .z-scrollbar-rail {
5 display: none;
6 }
7 .z-scrollbar-wrapper {
8 top: 0;
9 .z-scrollbar-indicator {
10 width: 7px;
11 background-image: none;
12 background-color: #999;
13 border: 0;
14 border-radius: 0;
15 }
16 .z-scrollbar-rail {
17 background-color: transparent;
18 }
19 }
20 }
Functionality Code Fragments
Although in most cases we don't have to write any code, we still need to declare some functions to manipulate components in some situations.
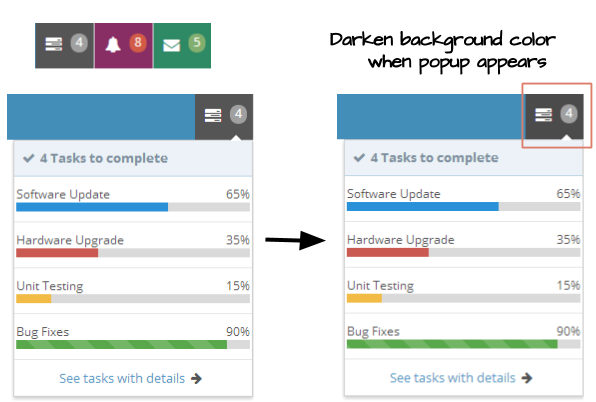
We declared an event handler in popup which will be notified when onOpen event occurs, it will toggle the open sclass to the anchor component. So the component's background will be darken when its popup is showing up.
<a id="atask" iconSclass="z-icon-tasks" popup="taskpp, position=after_end, type=toggle" sclass="grey">
<label value="4" sclass="badge badge-grey"/>
</a>
<popup id="notipp" sclass="menu menu-pink" width="240px">
...
</popup>
@Listen("onOpen = #taskpp")
public void toggleTaskPopup(OpenEvent event) {
toggleOpenClass(event.isOpen(), atask);
}
// Toggle open class to the component
public void toggleOpenClass(Boolean open, Component component) {
HtmlBasedComponent comp = (HtmlBasedComponent) component;
String scls = comp.getSclass();
if (open) {
comp.setSclass(scls + " open");
} else {
comp.setSclass(scls.replace(" open", ""));
}
}
Implement Collapse Mechanism
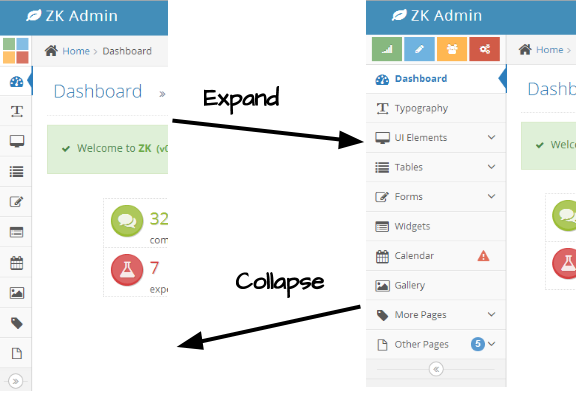
The sidebar in this demo is collapsible, user can click the button in the bottom of the navbar to collapse or expand the sidebar, illustrated in the picture below:
We need to declare toggleSidebarCollapsed() to proceed the action, like the following:
// Toggle sidebar to collapse or expand
@Listen("onClick = #toggler")
public void toggleSidebarCollapsed() {
if (navbar.isCollapsed()) {
sidebar.setSclass("sidebar");
navbar.setCollapsed(false);
calitem.setTooltip("calpp, position=end_center, delay=0");
toggler.setIconSclass("z-icon-angle-double-left");
} else {
sidebar.setSclass("sidebar sidebar-min");
navbar.setCollapsed(true);
calitem.setTooltip("");
toggler.setIconSclass("z-icon-angle-double-right");
}
// Force the hlayout contains sidebar to recalculate its size
Clients.resize(sidebar.getRoot().query("#main"));
}
Because Navbar is collapsible, isCollapsed() can determine whether navbar is collapsed or not. If not, we can easily call setCollapsed(true) to collapse it. When navbar is collapsed, its children will only appear as icon and badges. The text part will appear when you mouse hover the icon. Next, we need remove the tooltip of Navitem to prevent it from showing up with text when hovering. Then, add sidebar-min class to sidebar and change the toggler's icon. In the end, Clients.resize(sidebar.getRoot().query("#main")) will force the client to recalculate the size of the main content.
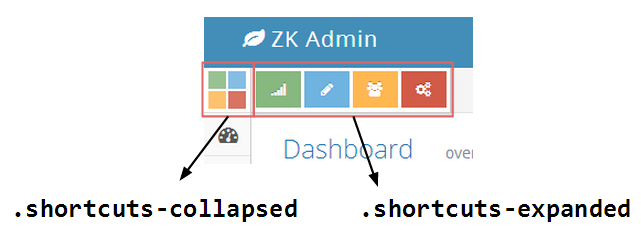
The shortcuts are also collapsed, so an additional set of collapsed shortcuts is needed for display when the sidebar is collapsed. If user mouses over the collapsed shortcuts, the shortcuts will expand.
<div class="shortcuts">
<div class="shortcuts-expanded">
<button type="button" class="btn-success" iconSclass="z-icon-signal"/>
<button type="button" class="btn-info" iconSclass="z-icon-pencil"/>
<button type="button" class="btn-warning" iconSclass="z-icon-group"/>
<button type="button" class="btn-danger" iconSclass="z-icon-cogs"/>
</div>
<div class="shortcuts-collapsed">
<button type="button" class="btn-success"/>
<button type="button" class="btn-info"/>
<button type="button" class="btn-warning"/>
<button type="button" class="btn-danger"/>
</div>
</div>
Conclusion
In this demo, we used ZK 7 with bootstrap and CSS3 to customize a bootstrap theme from scratch. We analyzed the template and implemented it with ZK components, then styled the look and feel using CSS3. This small talk shows you the power and flexibility of ZK 7's new theme system, and how you can customize your own personal or corporate theme with CSS3, LESS and bootstrap easily.
Example Source
Source code can be found in Github and the layout design is owned by EasyMind. Please contact the designer directly if you wish to use his design template commercially.
Reference
Comments
| Copyright © Potix Corporation. This article is licensed under GNU Free Documentation License. |