Chapter 2: Project Structure"
m (correct highlight (via JWB)) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| − | All source codes used in this book are available on [https://github.com/zkoss/zkessentials github]. As our example application has 3 different configurations, our source code is divided into 3 branches: '''master''', '''chapter9''', and '''chapter10'''. | + | All source codes used in this book are available on [https://github.com/zkoss/zkessentials github]. As our example application has 3 different configurations, our source code is divided into 3 branches: [https://github.com/zkoss/zkessentials/tree/master '''master'''], [https://github.com/zkoss/zkessentials/tree/chapter9 '''chapter9'''], and [https://github.com/zkoss/zkessentials/tree/chapter10 '''chapter10''']. |
[[File:Tutorial-ch2-3branches.png | center]] | [[File:Tutorial-ch2-3branches.png | center]] | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
= Project Structure= | = Project Structure= | ||
| − | The 2 images below show the project structure of the example application. It's Maven default project structure, and all main source codes are under < | + | The 2 images below show the project structure of the example application. It's Maven default project structure, and all main source codes are under <code>src/main</code>. The left image shows the Java source code is under <code>src/main/java</code> and the right one shows the web application content is under <code>src/main/webapp</code>. |
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
| − | We name the source code packages according to each chapter and each package contains the classes used in the example of that chapter. Some common classes are separated to an independent package as they are used in multiple chapters. The classes under < | + | We name the source code packages according to each chapter and each package contains the classes used in the example of that chapter. Some common classes are separated to an independent package as they are used in multiple chapters. The classes under <code>org.zkoss.essentials.entity.*</code> are entity class. We also define some business interfaces under <code>org.zkoss.essentials.service.*</code> and different chapters have different implementations. |
| − | For ZUL pages, we put them in an independent folder for each chapter under < | + | For ZUL pages, we put them in an independent folder for each chapter under <code>src/main/webapp/</code>. Under "WEB-INF" folder, '''web.xml''' contains minimal configuration to run ZK and for its detail please refer to [[ZK Installation Guide/Quick Start/Create and Run Your First ZK Application Manually| ZK Installation Guide \ Create and Run Your First ZK Application Manually]]. The "zk.xml" is optional configuration descriptor of ZK. Provide this file if you need to configure ZK differently from the default behavior. Refer to [[ZK Configuration Reference/zk.xml]] for more detail. |
= References = | = References = | ||
Latest revision as of 10:49, 19 January 2022
![]() This article is out of date, please refer to http://books.zkoss.org/zkessentials-book/master/ for more up to date information.
This article is out of date, please refer to http://books.zkoss.org/zkessentials-book/master/ for more up to date information.
Source Code
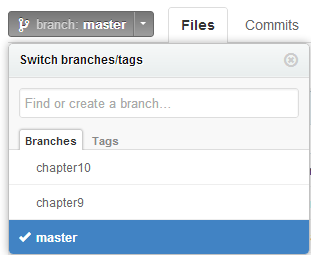
All source codes used in this book are available on github. As our example application has 3 different configurations, our source code is divided into 3 branches: master, chapter9, and chapter10.
The master branch contains examples from chapter 3 to chapter 8. The chapter9 branch has examples integrated with Spring and the chapter10 branch contains examples which integrate with Spring and use JPA to persist data into a database.
You can click the "ZIP" icon to download the current selected branch as a zip file.
Run Example Application
After you download the source code, you will find it is a Maven[1] project with jetty plugin configured. Therefore, if you have Maven, you can run the example application with a simple command[2] (The maven we use is 3.0.3). Navigate to the root folder of your downloaded source code, say it's "zkessentials" and type the command:
mvn jetty:run
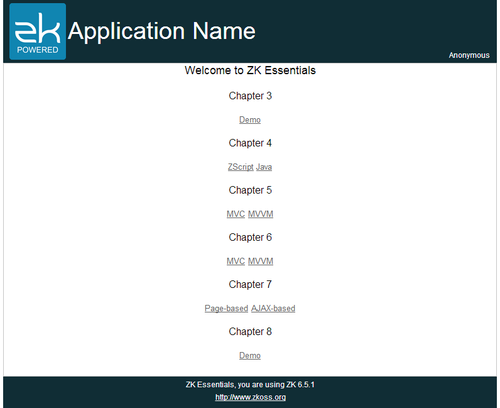
Then visit the URL http://localhost:8080/essentials/, and you should see the screen below.
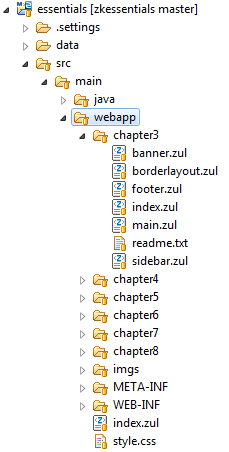
Project Structure
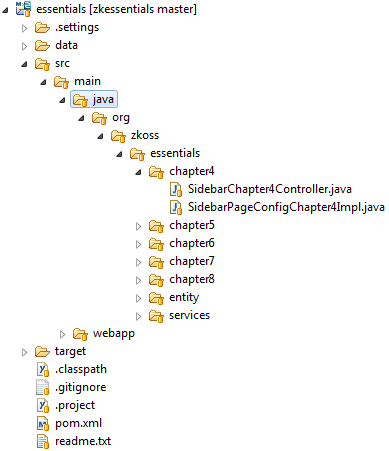
The 2 images below show the project structure of the example application. It's Maven default project structure, and all main source codes are under src/main. The left image shows the Java source code is under src/main/java and the right one shows the web application content is under src/main/webapp.
We name the source code packages according to each chapter and each package contains the classes used in the example of that chapter. Some common classes are separated to an independent package as they are used in multiple chapters. The classes under org.zkoss.essentials.entity.* are entity class. We also define some business interfaces under org.zkoss.essentials.service.* and different chapters have different implementations.
For ZUL pages, we put them in an independent folder for each chapter under src/main/webapp/. Under "WEB-INF" folder, web.xml contains minimal configuration to run ZK and for its detail please refer to ZK Installation Guide \ Create and Run Your First ZK Application Manually. The "zk.xml" is optional configuration descriptor of ZK. Provide this file if you need to configure ZK differently from the default behavior. Refer to ZK Configuration Reference/zk.xml for more detail.
References