Reference to Java Beans"
(→Usage) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
= Usage = | = Usage = | ||
| − | # | + | Steps to use this feature. |
| + | # Implement a variable resolver class. | ||
# Declare the variable resolver in ZUL pages or in system scope. | # Declare the variable resolver in ZUL pages or in system scope. | ||
Revision as of 08:07, 26 July 2013
Available in ZK Spreadsheet EE only
Overview
When showing data in Spreadsheet from backend, use Range API to set value cell by cell could be a tedious task. Hence, Spreadsheet allows you use EL (Expression Language) in cells and it resolves the name expressions to the back end Java beans automatically.
How Spreadsheet resolve a name in a cell
If a variable in cells equals Excel Defined Name[1] found in Excel file, ZK Spreadsheet will treat them as what it defines. If not, ZK Spreadsheet follows ZK's EL expression variable resolving mechanism. It first tries to find any matching zscript variables defined in the ZUL page. Then check ID of ZK fellow components. Then search in ZK components' attribute map. Finally ask variable resolvers defined in the zul page to retrieve the bean with named variable. If still none is found, it will return #NAME? as Excel's original behavior. Once variables are resolved, the associated getter are called and value returned in the cell.
Usage
Steps to use this feature.
- Implement a variable resolver class.
- Declare the variable resolver in ZUL pages or in system scope.
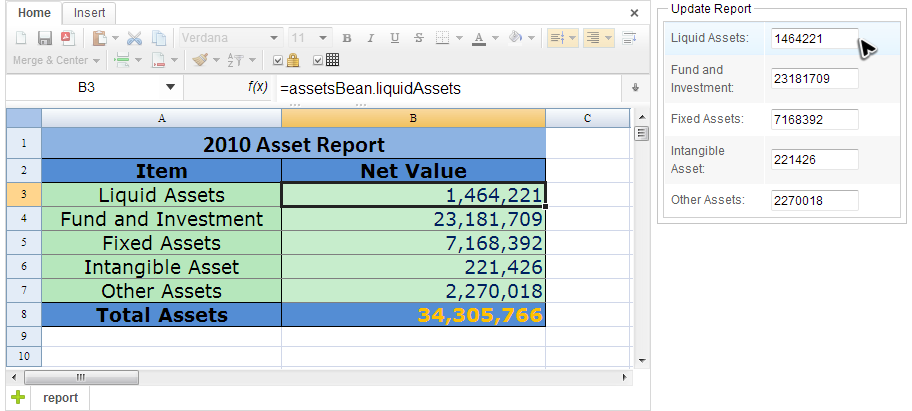
Then you can access JavaBeans like a formula, e.g. enter =myBean.myProperty in a cell.
Example
Assume the application below has a sheet in protection, a user cannot modify any cells directly in the sheet. They can only update value via panel on the right side.
public class RefBeanComposer extends SelectorComposer<Component> {
@Wire
private Spreadsheet ss;
@Wire
private Doublebox liquidBox;
@Wire
private Doublebox fundBox;
@Wire
private Doublebox fixedBox;
@Wire
private Doublebox intangibleBox;
@Wire
private Doublebox otherBox;
//initialize doublebox
@Listen("onChange = doublebox")
public void update() {
updateAssetsBean();
//notify spreadsheet about the bean's change
Ranges.range(ss.getSelectedSheet()).notifyChange(new String[] {"assetsBean"} );
}
/**
* load user input to the bean.
*/
private void updateAssetsBean() {
AssetsBean assetsBean = getAssetsBean();
assetsBean.setLiquidAssets(liquidBox.getValue());
assetsBean.setFundInvestment(fundBox.getValue());
assetsBean.setFixedAssets(fixedBox.getValue());
assetsBean.setIntangibleAsset(intangibleBox.getValue());
assetsBean.setOtherAssets(otherBox.getValue());
}
private AssetsBean getAssetsBean(){
AssetsBean assetsBean = (AssetsBean)getPage().getXelVariable("assetsBean");
return assetsBean;
}
}
- ↑ Defined Names is a name that represents a cell, range of cells, formula, or constant value.