Learn ZK in 10 Minutes"
| (30 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= What is ZK = | = What is ZK = | ||
| − | ZK is a UI framework that enables you to build amazing web and mobile applications without having to | + | ZK is a UI framework that enables you to build amazing web and mobile applications without having to write JavaScript or AJAX. |
= Fast UI Composition = | = Fast UI Composition = | ||
| − | Building UI with ZK is easy; simply combine and mix | + | Building UI with ZK is easy; simply combine and mix with the hundreds of components readily at hand. You can rapidly create your own user interface with various ZK components. Each component's style, behavior, and function can be configured upon your desire. |
| − | [[File:Getstarted-simpleZK-UI. | + | [[File:Getstarted-simpleZK-UI.jpeg | center]] |
| − | '''ZUL''', an XML-formatted and easy-to read language, is used to describe the above registration form | + | '''ZUL''', an XML-formatted and easy-to-read language, is used to describe the above registration form |
| − | < | + | <syntaxhighlight line lang="xml" highlight="1,2, 4, 18"> |
| − | + | <window border="normal" hflex="min" style="margin:0px auto;" title="Welcome! New User"> | |
| − | + | <grid id="formGrid" hflex="min" ctrlKeys="^h"> | |
| − | + | <auxhead> | |
| − | + | <auxheader colspan="2" label="Registration Form" iconSclass="z-icon-user-circle-o"/> | |
| − | + | </auxhead> | |
| − | + | <columns visible="false"> | |
| − | + | <column/> | |
| − | + | <column/> | |
| − | + | </columns> | |
| − | + | <rows> | |
| − | + | <row id="nameRow"> | |
| − | + | <!-- constraint="no empty" --> | |
| − | + | User Name | |
| − | + | <textbox id="nameBox" hflex="1" constraint="no empty"/> | |
| − | + | </row> | |
| − | + | <row> | |
| − | + | Gender: | |
| − | + | <radiogroup id="genderRadio"> | |
| − | + | <radio label="Male" value="male" iconSclass="z-icon-male" checked="true"/> | |
| − | + | <radio label="Female" value="female" iconSclass="z-icon-female"/> | |
| − | + | </radiogroup> | |
| − | + | </row> | |
| − | + | <row> | |
| − | + | Birthday | |
| − | + | <datebox id="birthdayBox" hflex="1" constraint="no empty, no today, no future"/> | |
| − | + | </row> | |
| − | + | <row spans="2" align="center"> | |
| − | + | <hlayout> | |
| − | + | <checkbox id="acceptTermBox"/> | |
| − | + | <label value=" Accept Term of Use (Click for detail)" popup="termDetail, position=end_after" | |
| − | + | style="cursor: pointer"/> | |
| − | + | </hlayout> | |
| − | + | </row> | |
| − | + | <row spans="2" align="right"> | |
| − | + | <hlayout> | |
| − | + | <label value="Help (Ctrl+h)"/> | |
| − | + | <button id="resetButton" label="Reset"/> | |
| − | + | <button id="submitButton" label="Submit" disabled="true"/> | |
| − | + | </hlayout> | |
| − | </ | + | </row> |
| − | * | + | </rows> |
| − | * ' | + | </grid> |
| + | ... | ||
| + | </window> | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | * Line 1: One tag represents one component. Some components can have child components. In this example, a ''window'' contains a ''grid''. | ||
| + | * Line 2: CSS flexible width, please see [[ZK%20Developer's%20Reference/UI%20Patterns/Hflex%20and%20Vflex]] | ||
| + | * Line 4: ZK contains [https://fontawesome.com/v4.7.0/icons/ font awesome icons] by default, you can specify icon CSS class at <code>iconSclass</code>. | ||
| + | * Line 18: You may give "id" attribute to a component, so you can control them in a Java controller. | ||
| − | ZK also allows you to create UI programmatically like how you use Java Swing within a | + | ZK also allows you to create UI programmatically like how you use Java Swing within a [[ZK%20Developer's%20Reference/UI%20Composing/Richlet | Richlet]]. |
| − | ZK UI components are like building blocks; you can combine, mix-match or inherit and make them into a new component to fulfill diverse requirements. This versatility increases reusability and modularity [[ | + | ZK UI components are like building blocks; you can combine, mix-match, or inherit and make them into a new component to fulfill diverse requirements. This versatility increases reusability and modularity. See [[ZK_Developer%27s_Reference/UI_Composing/Shadow_for_MVC | shadow elements]],[[ZK_Developer%27s_Reference/UI_Composing/Macro_Component | Macro]]. |
| Line 80: | Line 87: | ||
| − | To control the UI, firstly, you need to implement a controller class which inherits ZK's '''SelectorComposer''' | + | To control the UI, firstly, you need to implement a controller class which inherits ZK's [https://www.zkoss.org/javadoc/latest/zk/org/zkoss/zk/ui/select/SelectorComposer.html '''SelectorComposer'''] for a ZUL. Then, you can retrieve the UI component's Java object by annotating [[ZK%20Developer's%20Reference/MVC/Controller/Wire%20Components | '''@Wire''' on the controller's member variables]]. After this has been done, you can then control and manipulate UI by accessing those annotated member variables. |
| − | < | + | <syntaxhighlight line lang="java" highlight="7,10"> |
| − | package | + | package org.zkoss.simple; |
// some import statements are omitted for brevity. | // some import statements are omitted for brevity. | ||
| Line 97: | Line 104: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
* '''line 7,10''': Variable names "submitButton" and "acceptTermBox" corresponds to components' id attributes which are specified at mentioned ZUL in the previous section. | * '''line 7,10''': Variable names "submitButton" and "acceptTermBox" corresponds to components' id attributes which are specified at mentioned ZUL in the previous section. | ||
| Line 104: | Line 111: | ||
We can then use the controller above to control our UI components by specifying attribute "apply" in the ZUL. | We can then use the controller above to control our UI components by specifying attribute "apply" in the ZUL. | ||
| − | < | + | <syntaxhighlight line lang="xml" highlight="2"> |
<window border="normal" width="400px" title="Welcome! New User" | <window border="normal" width="400px" title="Welcome! New User" | ||
| − | apply=" | + | apply="org.zkoss.simple.RegistrationComposer"> |
<!-- omit other components for brevity --> | <!-- omit other components for brevity --> | ||
</window> | </window> | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
* '''Line 2:''' By applying the controller to the root component, you can control all child components inside the root component. | * '''Line 2:''' By applying the controller to the root component, you can control all child components inside the root component. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Handle User Action == | == Handle User Action == | ||
| Line 121: | Line 125: | ||
[[File:Simplezk-check-submit.gif | center]] | [[File:Simplezk-check-submit.gif | center]] | ||
| − | As ZK is an event-driven framework, user action is therefore handled by | + | As ZK is an event-driven framework, a user action is therefore handled by an event listener. ZK provides an annotation [[ZK%20Developer's%20Reference/MVC/Controller/Wire%20Event%20Listeners | '''@Listen''' to register an event listener by selector syntax]]. To achieve the above feature, you can annotate a method to listen to an "onCheck" event of "Accept Term of Use" checkbox. Whenever a user checks/unchecks the checkbox to trigger the "onCheck" event, ZK invokes the annotated method. We implement the above UI effect by changing the properties of a component (Java object) in the annotated method. |
| − | < | + | <syntaxhighlight line lang="java" highlight="14,17,18,20,21"> |
import org.zkoss.zk.ui.Component; | import org.zkoss.zk.ui.Component; | ||
import org.zkoss.zk.ui.select.SelectorComposer; | import org.zkoss.zk.ui.select.SelectorComposer; | ||
| Line 150: | Line 154: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
* '''line 14''': Use @Listen to declare a method to handle the ''onCheck'' event of "acceptTermBox". | * '''line 14''': Use @Listen to declare a method to handle the ''onCheck'' event of "acceptTermBox". | ||
* '''line 17,18''': Enable "Submit" button and display a checked icon when "Accept Term of Use" checkbox is checked. | * '''line 17,18''': Enable "Submit" button and display a checked icon when "Accept Term of Use" checkbox is checked. | ||
| Line 156: | Line 160: | ||
| − | With ZK's help, you can easily add fancy UI effects such as tooltip, drag & drop, and | + | With ZK's help, you can easily add fancy UI effects such as tooltip, drag & drop, and hotkey, etc. to your application. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == MVVM Pattern == | ||
| + | What we have introduced so far is MVC pattern, which controls UI by components API. Another way is data binding, please see [[ZK Getting Started/Get ZK Up and Running with MVVM| Get ZK Up and Running with MVVM]]. | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
| Line 164: | Line 172: | ||
Transparent Manipulation(client<-server) | Transparent Manipulation(client<-server) | ||
--> | --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Support Responsive Design = | ||
| + | ZK provides various features for you to apply responsive design, please read [[ZK_Developer%27s_Reference/UI_Patterns/Responsive_Design| Responsive Design]]. | ||
= Easy Backend Integration = | = Easy Backend Integration = | ||
| + | [[File: multi-layers.jpg | center]] | ||
| + | As ZK allows you to control UI via a controller on the server-side, the controller is, therefore, the main extension point to integrate any Java library or framework. To integrate ZK with other frameworks, write your controller code to use classes of back-end systems that construct your business or persistence layer. | ||
| − | |||
== Integrate Third-Party Library == | == Integrate Third-Party Library == | ||
| − | With the help of ZK's UI controller - '''SelectorComposer''', it is easy to integrate your legacy system service class, domain object, and any third party library such as Log4j. | + | With the help of ZK's UI controller - '''SelectorComposer''', it is easy to integrate your legacy system service class, domain object, and any third-party library such as Log4j. |
| − | < | + | <syntaxhighlight line lang="java" highlight="4,5,,6,11,12"> |
public class RegistrationIntegrateComposer extends SelectorComposer<Component> { | public class RegistrationIntegrateComposer extends SelectorComposer<Component> { | ||
| Line 181: | Line 193: | ||
//omit other variables for brevity | //omit other variables for brevity | ||
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(RegistrationIntegrateComposer.class.getName()); | private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(RegistrationIntegrateComposer.class.getName()); | ||
| − | private | + | private RegisterService registerService = new RegisterService(); |
private User newUser = new User(); | private User newUser = new User(); | ||
| Line 187: | Line 199: | ||
public void register(){ | public void register(){ | ||
//save user input into newUser object | //save user input into newUser object | ||
| − | + | registerService.add(newUser); | |
logger.debug("a user was added."); | logger.debug("a user was added."); | ||
//... | //... | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
* '''Line 4,12:''' Call Log4j to log error. | * '''Line 4,12:''' Call Log4j to log error. | ||
| − | * '''Line 5,11:''' Use your | + | * '''Line 5,11:''' Use your service object in the controller. |
* '''Line 6,11:''' Use your own domain object. | * '''Line 6,11:''' Use your own domain object. | ||
| Line 206: | Line 218: | ||
| − | < | + | <syntaxhighlight line lang="java" highlight="1,4,10"> |
@VariableResolver(org.zkoss.zkplus.spring.DelegatingVariableResolver.class) | @VariableResolver(org.zkoss.zkplus.spring.DelegatingVariableResolver.class) | ||
| Line 221: | Line 233: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| − | * '''Line 1:''' To use CDI, simply use another resolver: < | + | * '''Line 1:''' To use CDI, simply use another resolver: <code> org.zkoss.zkplus.cdi.DelegatingVariableResolver.class </code>. |
| − | * '''Line 4:''' For those variables with < | + | * '''Line 4:''' For those variables with <code> @WireVariable </code>, ZK will inject qualified Spring beans by retrieving them from Spring context with variable resolver. |
| + | |||
| + | = Work with Spring-boot= | ||
| + | ZK provides a zkspringboot-starter addon to help you work with Springboot easily, please refer to [[ZK_Installation_Guide/Quick_Start/Create_and_Run_Your_First_ZK_Application_with_Spring_Boot| Create and Run Your First ZK Application with Spring Boot]]. | ||
= Source Code = | = Source Code = | ||
| − | You can get the complete source code mentioned in this page at [https://github.com/zkoss-demo/gettingStarted/tree/master | + | You can get the complete source code mentioned in this page at [https://github.com/zkoss-demo/gettingStarted/tree/master github] |
| + | |||
| + | <references/> | ||
= What's Next = | = What's Next = | ||
| − | = | + | <ul class="h3"> |
| − | [[ZK_Installation_Guide/Quick_Start| Quick Start]] with | + | <li>[[ZK_Installation_Guide/Quick_Start| Quick Start]] |
| − | + | <ul> | |
| − | + | <li class="h6">Start to develop with ZK with your familiar tools including Eclipse, IntelliJ, NetBean, Maven, Gradle, or Spring Boot.</li> | |
| − | [[ZK Getting Started/Get ZK Up and Running with MVC| Start MVC]] | + | </ul> |
| − | + | </li> | |
| − | + | <li>[[ZK Getting Started/Get ZK Up and Running with MVC| Start in MVC pattern]] </li> | |
| − | [[ZK Getting Started/Get ZK Up and Running with MVVM| Start MVVM]] | + | <li>[[ZK Getting Started/Get ZK Up and Running with MVVM| Start in MVVM pattern]]</li> |
| − | + | <li>[http://www.zkoss.org/zkdemo/ ZK Demo]</li> | |
| − | + | </ul> | |
| − | [http://www.zkoss.org/zkdemo/ ZK Demo] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:22, 24 May 2023
What is ZK
ZK is a UI framework that enables you to build amazing web and mobile applications without having to write JavaScript or AJAX.
Fast UI Composition
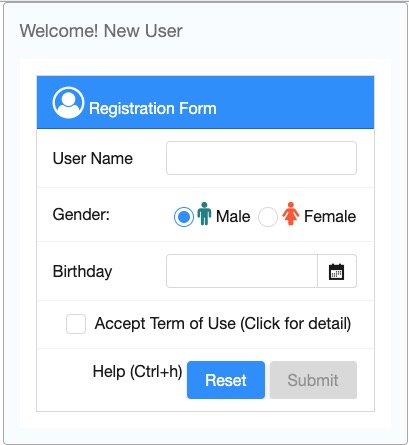
Building UI with ZK is easy; simply combine and mix with the hundreds of components readily at hand. You can rapidly create your own user interface with various ZK components. Each component's style, behavior, and function can be configured upon your desire.
ZUL, an XML-formatted and easy-to-read language, is used to describe the above registration form
1 <window border="normal" hflex="min" style="margin:0px auto;" title="Welcome! New User">
2 <grid id="formGrid" hflex="min" ctrlKeys="^h">
3 <auxhead>
4 <auxheader colspan="2" label="Registration Form" iconSclass="z-icon-user-circle-o"/>
5 </auxhead>
6 <columns visible="false">
7 <column/>
8 <column/>
9 </columns>
10 <rows>
11 <row id="nameRow">
12 <!-- constraint="no empty" -->
13 User Name
14 <textbox id="nameBox" hflex="1" constraint="no empty"/>
15 </row>
16 <row>
17 Gender:
18 <radiogroup id="genderRadio">
19 <radio label="Male" value="male" iconSclass="z-icon-male" checked="true"/>
20 <radio label="Female" value="female" iconSclass="z-icon-female"/>
21 </radiogroup>
22 </row>
23 <row>
24 Birthday
25 <datebox id="birthdayBox" hflex="1" constraint="no empty, no today, no future"/>
26 </row>
27 <row spans="2" align="center">
28 <hlayout>
29 <checkbox id="acceptTermBox"/>
30 <label value=" Accept Term of Use (Click for detail)" popup="termDetail, position=end_after"
31 style="cursor: pointer"/>
32 </hlayout>
33 </row>
34 <row spans="2" align="right">
35 <hlayout>
36 <label value="Help (Ctrl+h)"/>
37 <button id="resetButton" label="Reset"/>
38 <button id="submitButton" label="Submit" disabled="true"/>
39 </hlayout>
40 </row>
41 </rows>
42 </grid>
43 ...
44 </window>
- Line 1: One tag represents one component. Some components can have child components. In this example, a window contains a grid.
- Line 2: CSS flexible width, please see ZK Developer's Reference/UI Patterns/Hflex and Vflex
- Line 4: ZK contains font awesome icons by default, you can specify icon CSS class at
iconSclass. - Line 18: You may give "id" attribute to a component, so you can control them in a Java controller.
ZK also allows you to create UI programmatically like how you use Java Swing within a Richlet.
ZK UI components are like building blocks; you can combine, mix-match, or inherit and make them into a new component to fulfill diverse requirements. This versatility increases reusability and modularity. See shadow elements, Macro.
Intuitive UI Controlling
ZK is a component-based framework with event-driven programming model, therefore, developers add functions to respond to events of components that are triggered by users interaction.
UI Controller
To control the UI, firstly, you need to implement a controller class which inherits ZK's SelectorComposer for a ZUL. Then, you can retrieve the UI component's Java object by annotating @Wire on the controller's member variables. After this has been done, you can then control and manipulate UI by accessing those annotated member variables.
1 package org.zkoss.simple;
2
3 // some import statements are omitted for brevity.
4
5 public class RegistrationComposer extends SelectorComposer<Component> {
6
7 @Wire
8 private Button submitButton;
9
10 @Wire
11 private Checkbox acceptTermBox;
12 }
- line 7,10: Variable names "submitButton" and "acceptTermBox" corresponds to components' id attributes which are specified at mentioned ZUL in the previous section.
We can then use the controller above to control our UI components by specifying attribute "apply" in the ZUL.
1 <window border="normal" width="400px" title="Welcome! New User"
2 apply="org.zkoss.simple.RegistrationComposer">
3 <!-- omit other components for brevity -->
4 </window>
- Line 2: By applying the controller to the root component, you can control all child components inside the root component.
Handle User Action
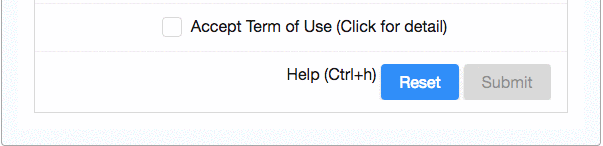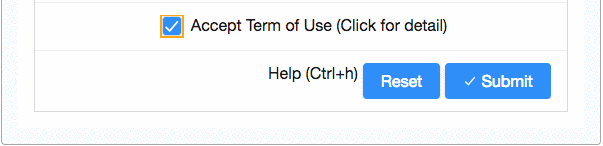
In the registration form above, the "Submit button" is disabled at the beginning, and it is only enabled (clickable) when a user checks the "Term of use" checkbox.
As ZK is an event-driven framework, a user action is therefore handled by an event listener. ZK provides an annotation @Listen to register an event listener by selector syntax. To achieve the above feature, you can annotate a method to listen to an "onCheck" event of "Accept Term of Use" checkbox. Whenever a user checks/unchecks the checkbox to trigger the "onCheck" event, ZK invokes the annotated method. We implement the above UI effect by changing the properties of a component (Java object) in the annotated method.
1 import org.zkoss.zk.ui.Component;
2 import org.zkoss.zk.ui.select.SelectorComposer;
3 import org.zkoss.zk.ui.select.annotation.Listen;
4 import org.zkoss.zk.ui.select.annotation.Wire;
5 import org.zkoss.zul.Button;
6 import org.zkoss.zul.Checkbox;
7
8 public class RegistrationComposer extends SelectorComposer<Component> {
9 @Wire
10 private Button submitButton;
11 @Wire
12 private Checkbox acceptTermBox;
13
14 @Listen("onCheck = #acceptTermBox")
15 public void changeSubmitStatus(){
16 if (acceptTermBox.isChecked()){
17 submitButton.setDisabled(false);
18 submitButton.setImage("/images/submit.png");
19 }else{
20 submitButton.setDisabled(true);
21 submitButton.setImage("");
22 }
23 }
24
25 }
- line 14: Use @Listen to declare a method to handle the onCheck event of "acceptTermBox".
- line 17,18: Enable "Submit" button and display a checked icon when "Accept Term of Use" checkbox is checked.
- line 20,21: Disable "Submit" button and clear the checked icon.
With ZK's help, you can easily add fancy UI effects such as tooltip, drag & drop, and hotkey, etc. to your application.
MVVM Pattern
What we have introduced so far is MVC pattern, which controls UI by components API. Another way is data binding, please see Get ZK Up and Running with MVVM.
Support Responsive Design
ZK provides various features for you to apply responsive design, please read Responsive Design.
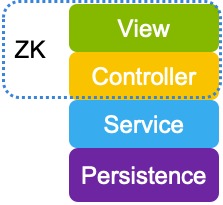
Easy Backend Integration
As ZK allows you to control UI via a controller on the server-side, the controller is, therefore, the main extension point to integrate any Java library or framework. To integrate ZK with other frameworks, write your controller code to use classes of back-end systems that construct your business or persistence layer.
Integrate Third-Party Library
With the help of ZK's UI controller - SelectorComposer, it is easy to integrate your legacy system service class, domain object, and any third-party library such as Log4j.
1 public class RegistrationIntegrateComposer extends SelectorComposer<Component> {
2
3 //omit other variables for brevity
4 private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(RegistrationIntegrateComposer.class.getName());
5 private RegisterService registerService = new RegisterService();
6 private User newUser = new User();
7
8 @Listen("onClick = #submitButton")
9 public void register(){
10 //save user input into newUser object
11 registerService.add(newUser);
12 logger.debug("a user was added.");
13 //...
14 }
15 }
- Line 4,12: Call Log4j to log error.
- Line 5,11: Use your service object in the controller.
- Line 6,11: Use your own domain object.
Integrate Business and Persistence Layer Framework
It is very important that a UI framework can cooperate with other business or persistence layer frameworks when building a multi-tier web application. ZK is easily integratable with business layer frameworks like Spring.
Assume you have implemented some classes according to Data Access Object (DAO) pattern as your application's persistence layer with Hibernate, JPA or other persistence framework. It is in your controller that you should use these classes to implement your application's feature.
1 @VariableResolver(org.zkoss.zkplus.spring.DelegatingVariableResolver.class)
2 public class RegistrationSpringComposer extends SelectorComposer<Component> {
3
4 @WireVariable
5 private RegistrationDao registrationDao;
6
7 @Listen("onClick = #submitButton")
8 public void submit(){
9 // omit irrelevant code for brevity
10 registrationDao.add(newUser);
11 }
12 }
- Line 1: To use CDI, simply use another resolver:
org.zkoss.zkplus.cdi.DelegatingVariableResolver.class. - Line 4: For those variables with
@WireVariable, ZK will inject qualified Spring beans by retrieving them from Spring context with variable resolver.
Work with Spring-boot
ZK provides a zkspringboot-starter addon to help you work with Springboot easily, please refer to Create and Run Your First ZK Application with Spring Boot.
Source Code
You can get the complete source code mentioned in this page at github
What's Next
- Quick Start
- Start to develop with ZK with your familiar tools including Eclipse, IntelliJ, NetBean, Maven, Gradle, or Spring Boot.
- Start in MVC pattern
- Start in MVVM pattern
- ZK Demo